
Aircraft investigation >>>>>>> HOME PAGE
weight and performance calculations for the McDonnel Douglas MD-82
***** PRELIMINARY FILE ****

McDonnel Douglas MD-82
role : jet airliner
importance : ****
first flight : 8 January 1981 operational : August 1981 (Republic airlines)
country : United States of America
design :
production : 569 aircraft (includinD-82T) total MD-80 production : 1191 aircraft.
general information :
The MD-80 series was developed as follow up for the DC-9 series, it had JT8D-200
engines with higher bypass for better economics and noise reduction. The fuselage is
stretched with 4.3 [m] from the DC-9-50 and it has a 28% larger wing.
The MD-82 is a variant with more powerful engines for operating from “hot & high”
airfields but also with better payload-range under normal conditions.
American Airlines was the world's largest operator of the MD-82, with at one point over
300 MD-82s in the fleet.
Due to the use of the aging JT8D engines, the MD-80 is not fuel efficient compared to the A320 or newer 737 models; it burns 1,050 US gal (4,000 L) of jet fuel per hour on a typical flight, while the larger Boeing 737-800 burns 850 US gal (3,200 L) per hour (19% reduction). In the 2000s many airlines began to retire the type. Alaska Airlines' tipping point in using the 737-800 was the $4 per gallon price of jet fuel the airline was paying by the summer of 2008; the airline stated that a typical Los Angeles-Seattle flight would cost $2,000 less, using a Boeing 737-800, than the same flight using an MD-80.
In late March 2008 and again in early April 2008, an FAA safety audit of American Airlines forced the airline to ground all its MD-80 series aircraft (approximately 300) to inspect the wiring for one of the aircraft's hydraulic systems. This led to American cancelling nearly 2,500 flights in March and over 3,200 in April. In addition, Delta Air Lines voluntarily inspected its own MD-80 fleet to ensure its 117 MD-80s were also operating within regulation. This resulted in Delta cancelling 275 flights. (source : Wikipedia)
In August 2022 still 116 MD-80 were in service.
primary users : American Airlines, Alitalia, Republic Airlines, Meridiana, Spanair, Balair,
Bulgarian Air
Accommodation:
flight crew : 2 cabin crew : 5
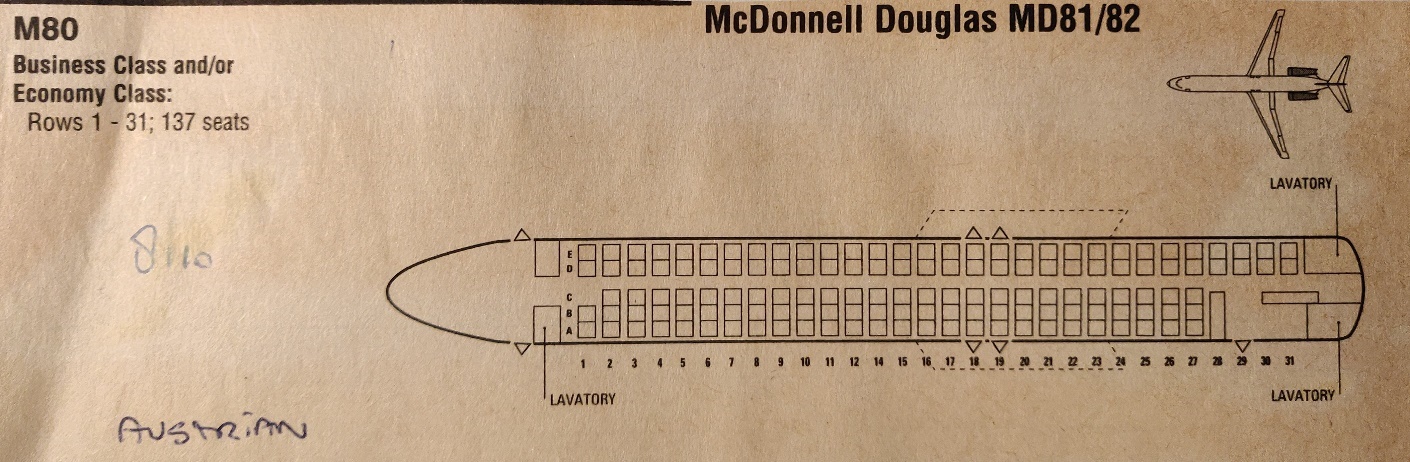
passengers : seating for 143 in two class : 12 business class and 131 economy class seats
( 32 -in pitch)
exit limit : 172 passengers
engine : 2 Pratt & Whitney JT8D-217 turbofan engines of 89.0 [KN] (20007.7 [lbf])
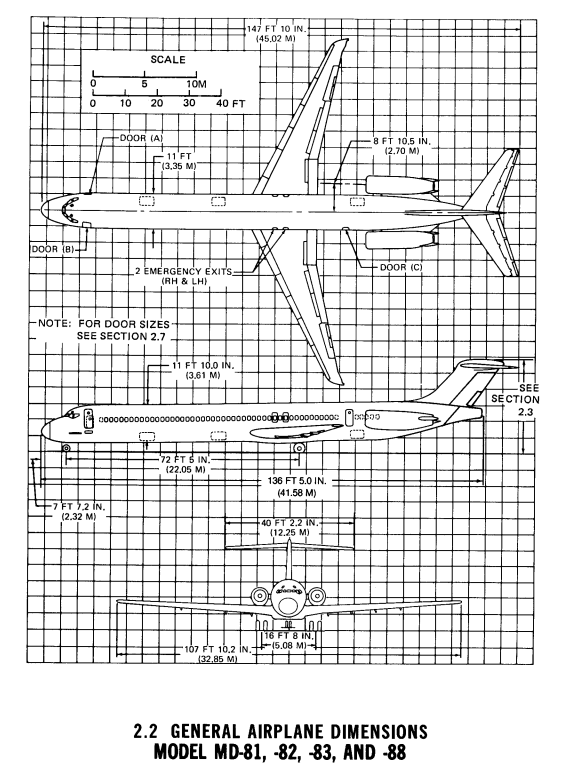
dimensions :
wingspan : 32.85 [m], length : 45.02 [m], height : 9.02 [m]
wing area : 112.3 [m^2] fuselage exterior width : 3.34 [m]
weights :
operating empty weight : 35369 [kg] max. structural payload : 19969 [kg]
Zero Fuel weight (ZFW) : 55338 [kg] max. landing weight (MLW) : 58967 [kg]
max.take-off weight : 67812 [kg] weight fuel : 17703 [kg] (22129 [liter])
performance :
Max. operating Mach number (Mmo) : 0.83 [Mach] (927 [km/hr]) at 7620 [m]
normal cruise speed : 873 [km/hr] (Mach 0.80 ) at 9150 [m] (34 [%] power)
economic cruise speed : 830 [km/hr] (Mach 0.76 ) at 9150 [m]
service ceiling : 11278 [m]
range with max fuel : 3800 [km] (ATA domestic fuel reserves - 370.0 [km] alternate)
description :
low-wing cantilever monoplane with retractable landing gear with nose wheel
two main spar fail-safe wing structure
with double slotted flaps with full-span slotted LE flaps (slats) ,with spoilers airfoil : NACA
sweep angle 3/4 chord: 24.5 [°]
engines attached to the tail, landing gear attached to the wings, fuel tanks in the wings
fuselage shape : 0 construction : all-metal aluminium-alloy stressed-skin construction with pressurized fuselage
calculation : *1* (dimensions)
wing chord at root : 7.05 [m]
mean wing chord : 3.42 [m]
calculated average wing chord tapered wing with rounded tips: 3.39 [m]
wing aspect ratio : 9.61 []
seize (span*length*height) : 13340 [m^3]
calculation : *2* (fuel consumption)
oil consumption : 17.8 [kg/hr]
fuel consumption (econ. cruise speed) : 3523.7 [kg/hr] (4404.6 [litre/hr]) at 32 [%] power
distance flown for 1 kg fuel : 0.24 [km/kg] at 9150 [m] height, sfc : 61.0 [kg/KN/h]
total fuel capacity : 22129 [litre] (17703 [kg])
calculation : *3* (weight)
weight engine(s) dry : 4162.0 [kg] = 23.38 [kg/KN]
weight 123 litre oil tank : 10.48 [kg]
oil tank filled with 1.1 litre oil : 1.0 [kg]
oil in engine 2.2 litre oil : 2.0 [kg]
fuel in engine 9.7 litre fuel : 7.12 [kg]
weight fuel lines 43.6 [kg]
weight engine cowling 462.8 [kg]
weight thrust reversers 71.2 [kg]
total weight propulsion system : 4760 [kg](7.0 [%])
***************************************************************
Accommodation cabin facilities:
typical 2-class cabin layout for 143 passengers : economy : pitch : 81.3 [cm] 32.0 [-in]
( 3+2 ) seating in 29.2 rows
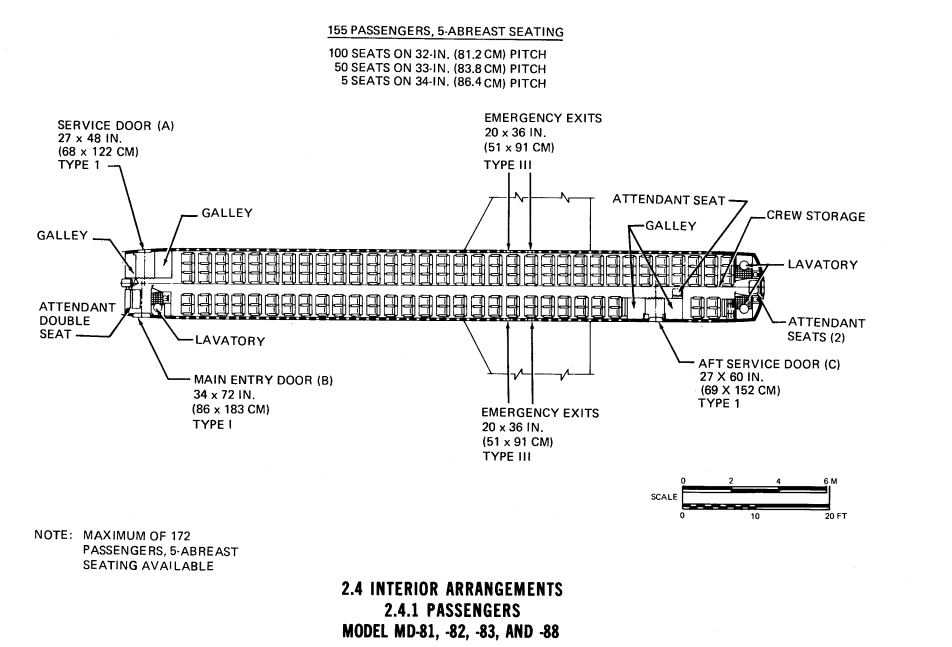
weight seats : 750.0 [kg]
high density seating passengers : 170 [pax] at 5 -abreast seating in 33.9 rows, pitch 73.7 [cm] 29.0 [-in]
pax density, normal seating : 0.65 [m2/pax], high density seating : 0.55 [m2/pax]
weight 3 lavatories : 43.3 [kg]
weight 2 galleys : 133.6 [kg]
weight overhead stowage for hand luggage : 50.0 [kg]
weight 3 wardrobe closets : 28.6 [kg]
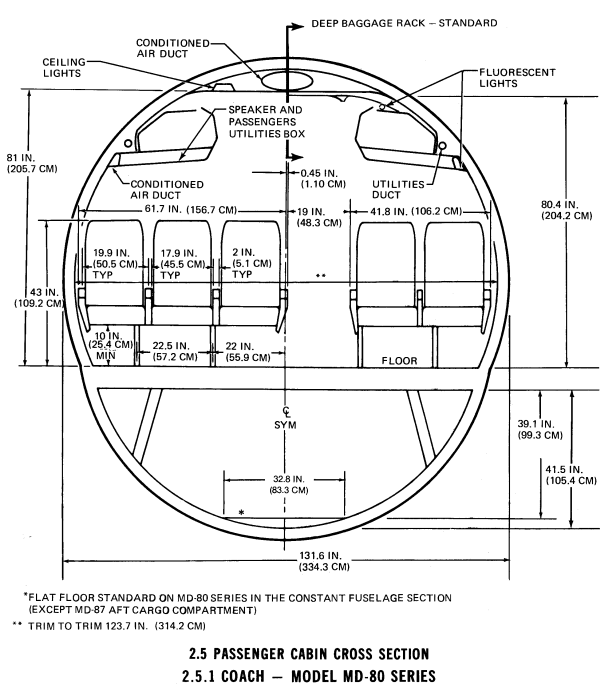
weight 60 windows : 54.4 [kg]
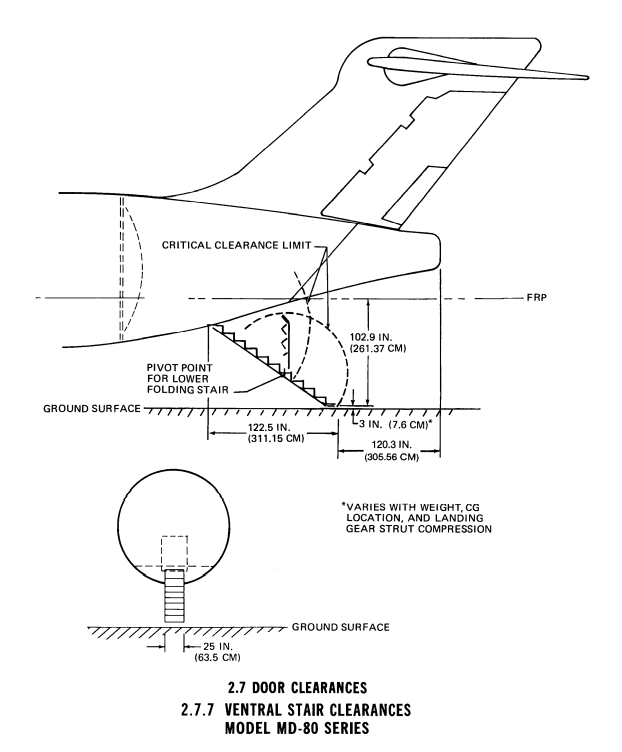
weight 4 1.83x0.86 [m] entrance/exit doors : 162.4 [kg]
weight tail entrance stairs : 83.5 [kg]
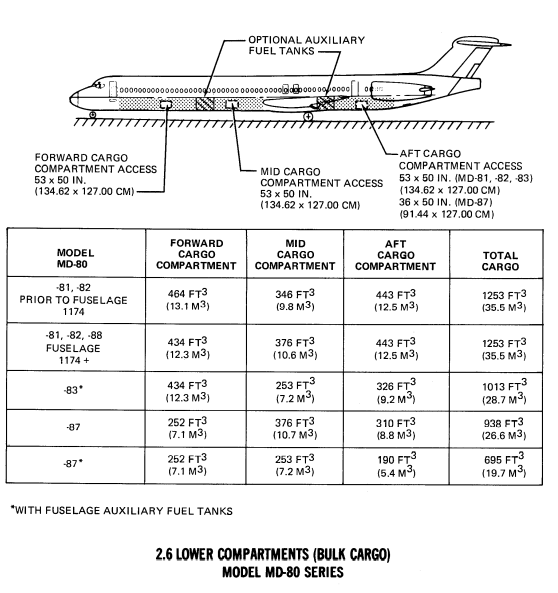
weight 3 (134.6x127 cm) freight doors (belly) : 132.3 [kg]
belly baggage/cargo hold volume front : 12.33 [m3]
belly baggage/cargo hold volume middle : 10.59 [m3]
belly baggage/cargo hold volume rear : 12.51 [m3]
passenger compartment volume : 111 [m3]
passenger cabin max.width : 3.11 [m] cabin length : 30.75 [m] cabin height : 2.06 [m]
floor area : 92.7 [m2]
weight cabin facilities : 1354.6 [kg]
safety facilities:
weight 4 over wing emergency exits (91x51 cm): 77.4 [kg]
weight 7 hand fire extinguisher : 22 [kg]
weight cockpit voice recorder (CVR) and flight data recorder (FDR): 20.0 [kg]
weight oxygen masks & oxygen generators : 93.0 [kg]
weight emergency flare installation : 10 [kg]
weight 3 emergency evacuation slides : 81.4 [kg]
weight safety equipment & facilities : 387 [kg]
fuselage construction:
fuselage aluminium frame : 8252 [kg]
floor loading (payload/m2): 215 [kg/m2]
weight rear pressure bulkhead : 106.9 [kg]
fuselage covering ( 319.9 [m2] duraluminium 2.37 [mm]) : 1980.0 [kg]
weight floor beams : 346.2 [kg]
weight cabin furbishing : 682.2 [kg]
weight cabin floor : 1236.3 [kg]
fuselage (sound proof) isolation : 230.1 [kg]
weight empty waste tank : 14 [kg]
weight engine mounts : 89 [kg]
weight fuselage structure : 12936.5 [kg]
Avionics:
weight HF and UHF radio : 7.0 [kg]
weight dual cloud-collision radar : 25.0 [kg]
weight VOR/ILS,RMI,Doppler,radio altimeter : 12.0 [kg]
weight Integrated Flight System / auto-pilot : 23.0 [kg]
weight artificial horizons, compass, alti-meters : 7 [kg]
weight engine monitoring gauges & control switches : 6 [kg]
weight avionics : 80.0 [kg]
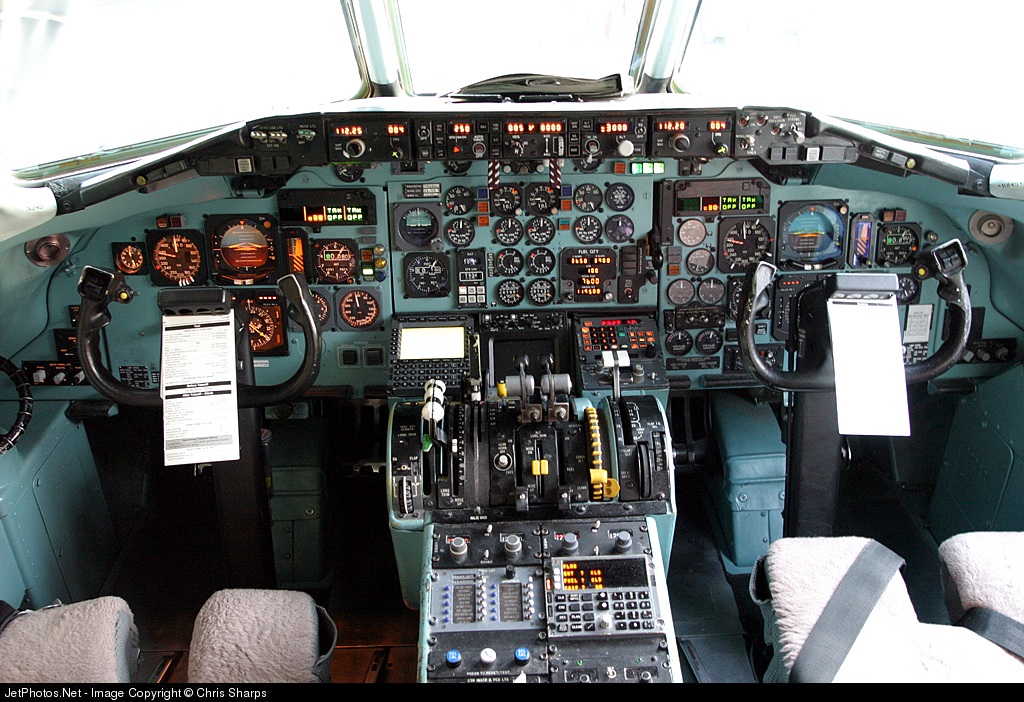

American Airlines MD-82 cockpit, N249AA
Systems:
Air-conditioning and pressurisation system maintains sea level conditions up to 5900 [m]
and gives equivalent of 2250 [m] at 10700 [m]. pressure differential : 0.54 [bars] (kg/cm2)
pressurized fuselage volume : 317 [m3]
weight air-conditioning and pressurisation system : 178 [kg]
weight APU / engine starter: 44.5 [kg]
weight lighting : 47.2 [kg]
weight engine-driven 40kVA electricity generators : 35.8 [kg]
weight controls : 18.2 [kg]
weight systems : 323.4 [kg]
total weight fuselage : 15081 [kg](22.2 [%])
***************************************************************
total weight aluminium ribs (1013 ribs) : 2418 [kg]
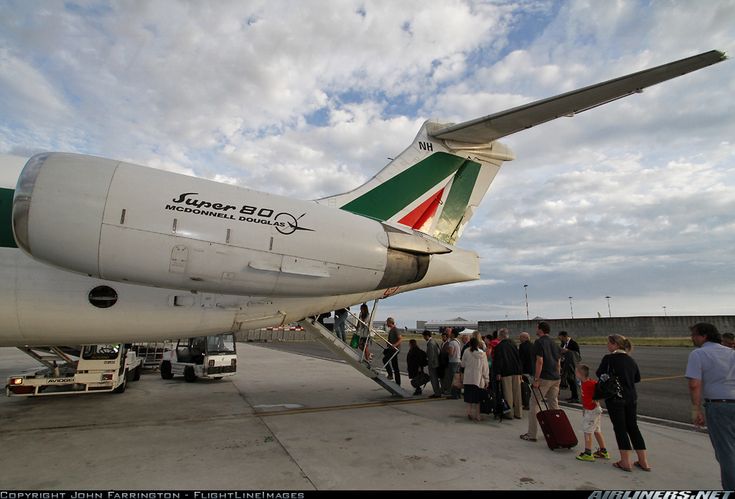

Alitalia MD-82, boarding via the tail stairs.
weight 7 fuel tanks empty for total 22129 [litre] fuel : 1239 [kg]
weight wing covering (painted aluminium 3.27 [mm]) : 1982 [kg]
total weight aluminium spars (multi-cellular wing structure) : 2059 [kg]
weight wings : 6459 [kg]
weight wing/square meter : 57.52 [kg]
weight thermal leading-edge anti-icing : 36.1 [kg]
weight ailerons (3.5 [m2]) : 101.8 [kg]
weight fin (15.0 [m2]) : 866.8 [kg]
weight rudder (6.1 [m2]) : 168.0 [kg]
weight tailplane (stabilizer) (29.2 [m2]): 1178.6 [kg]
weight elevators (9.8 [m2]): 152.3 [kg]
weight flight control hydraulic servo actuators: 57.8 [kg]
weight trailing-edge double slotted flaps (19.6 [m2]) : 484.7 [kg]
weight leading edge slats (11.2 [m2]) : 180.2 [kg]
weight spoilers (3.2 [m2]) : 51.2 [kg]
total weight wing surfaces & bracing : 10976 [kg] (16.2 [%])
*******************************************************************
tyre pressure main wheels : 12.9 [Bar] (nitrogen), ply rating : 26 PR
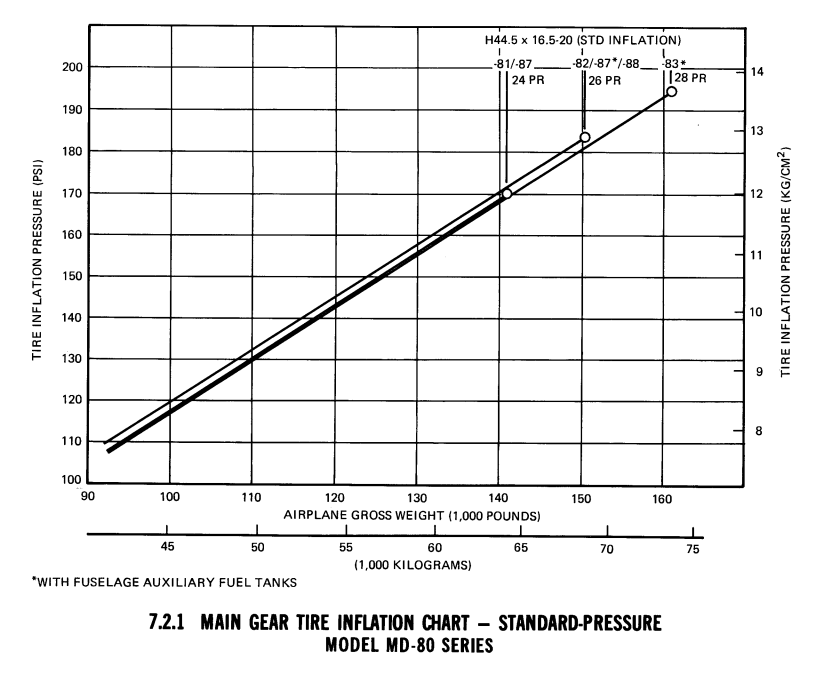
Diagram showing the correlation between wheel pressure (airplane gross weight) and tire inflation pressure. With the higher weights and tire pressure also the ply-rating must be higher, rising from 24PR to 28PR. The ply-rating is an indication for the tyre strength.
tyre speed limit: 364 [km/hr]
Can only operate from paved runways
wheel pressure : 14918.6 [kg]
weight 4 Dunlop main wheels (1130 [mm] by 420 [mm]) : 514.4 [kg]
weight 2 nose wheels : 128.6 [kg]
weight multi-disc wheel-brakes : 55.3 [kg]
weight flywheel detector type anti-skid units : 5.4 [kg]
weight oleo-pneumatic shock absorbers : 73.8 [kg]
weight wheel hydraulic operated retraction system : 654.3 [kg]
weight undercarriage struts with axle 1806.8 [kg]
total weight landing gear : 3238.6 [kg] (4.8 [%]
*******************************************************************
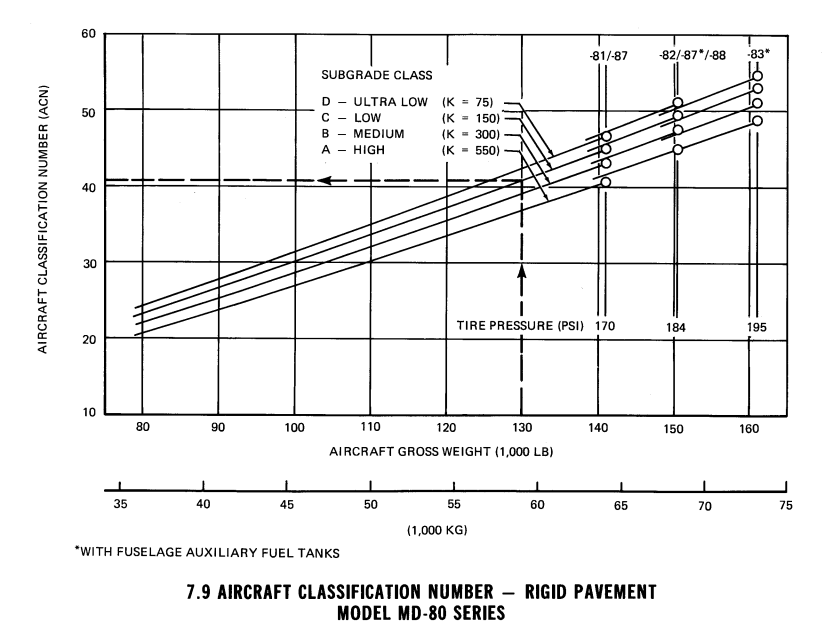
The Aircraft Classification Number (ACN) compared with the Pavement Classification Number (PCN) makes it possible to know for a pilot if he can land on a specific airport. This is useful in case of a diversion is needed to another airport.
The PCN code for a specific runway at an airport reeds as follows (example is for Tashkent apt, Uzbekistan) :
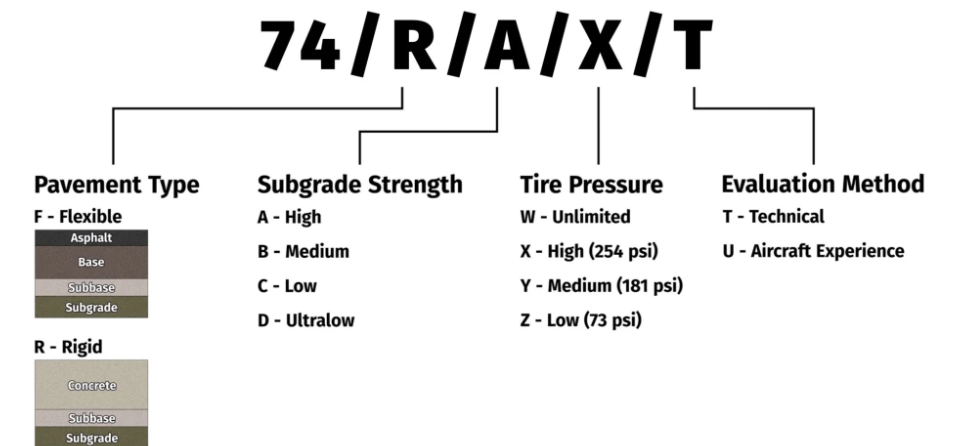
So this PCN nr is for a rigid payment (R) with high subgrade strength (A), suitable for high pressure tyres (X) based on technical calculations (T). The ACN for the MD-82 on a rigid pavement, at 68000 kg gross weight, high subgrade is about 45, so far below PCN 74 for this runway. So it can land without problem.
********************************************************************
calculated empty weight : 34056 [kg](50.2 [%])
weight oil for 5.2 hours flying : 107.3 [kg]
weight lifejackets : 64.4 [kg]
weight 3 life rafts : 89.4 [kg]
weight catering : 222.7 [kg]
weight water : 178.2 [kg]

Meridiana MD-82 interior, I-SMEL
weight crew : 567 [kg]
weight crew lugage,nav.chards,flight doc.,miscell.items : 84 [kg]
operational weight empty : 35369 [kg] (52.2 [%])
********************************************************************
weight 143 passengers : 11011 [kg]
weight luggage : 2288 [kg]
weight cargo : 6670 [kg] (cargo+luggage/m3 belly : 237 [kg/m3])
zero fuel weight (ZFW): 55338 [kg](81.6 [%])
weight fuel for landing (1.0 hours flying) : 3629 [kg]
max. landing weight (MLW): 58967 [kg](87.0 [%])
max. fuel weight : 53072 [kg] (78.3 [%])
payload with max fuel : 158 passengers+luggage 14740 [kg]
published maximum take-off weight : 67812 [kg] (100.0 [%])
calculation : * 4 * (engine power)
power loading (Take-off) : 381 [kg/KN]
power loading (Take-off) 1 PUF: 762 [kg/KN]
max. total take-off power : 178.0 [KN]
calculation : *5* (loads)
manoeuvre load : 6.6 [g] at 1000 [m]
limit load : 3.0 [g] ultimate load : 4.5 [g] load factor : 1.0 [g]
design flight time : 3.11 [hours]

On starboard side the MD-82 does not have an aft service door. Here is Air Adriatic MD-82 9A-CBC accelerating for take off.
design cycles : 14923 sorties, design hours : 46485 [hours]
max. wing loading (MTOW & flaps retracted) : 604 [kg/m2]
wing stress (2 g) during operation : 192 [N/kg] at 2g emergency manoeuvre
calculation : *6* (angles of attack)
angle of attack zero lift : -1.68 ["]
max. angle of attack (stalling angle, clean) : 13.30 ["]
max. angle of attack (full flaps) : 17.50 ["]
angle of attack at max. speed : 1.73 ["]
calculation : *7* (lift & drag ratios
lift coefficient at angle of attack 0° : 0.15 [ ]
lift coefficient at max. speed : 0.30 [ ]
lift coefficient at max. angle of attack : 1.34 [ ]
max. lift coefficient full flaps : 2.36 [ ]
drag coefficient at max. speed : 0.0384 [ ]
drag coefficient at econ. cruise speed : 0.0423 [ ]
induced drag coefficient at econ. cruise speed : 0.0079 [ ]
drag coefficient (zero lift) : 0.0344 [ ]
lift/drag ratio at max. speed : 7.91 [ ]
calculation : *8* (speeds
take-off safety speed (V2) : 259 [km/u]
take-off (initial climb) speed (Vto) : 309 [km/u]
stalling speed clean at sea-level (OW loaded : 64288 [kg]): 298 [km/u]
max. rate of climb speed : 486 [km/hr] at sea-level
max. endurance speed (Vbe): 422 [km/u] min. fuel/hr : 2748 [kg/hr] at height : 3658 [m]
max. range speed (Vbr): 831 [km/u] min. fuel consumption : 3.819 [kg/km] at cruise
height : 10668 [m]
cruising speed : 873 [km/hr] at 9150 [m] (power:35 [%])
max. operational speed (Mmo) : 927.00 [km/hr] (Mach 0.83 ) at 7620 [m] (power:43.5 [%])
airflow at cruise speed per engine : 136.3 [kg/s]
speed of thrust jet : 1688 [km/hr]
initial descent speed 10000 - 7315 [m]: Mach 0.75
descent speed 7315 - 3048 [m]: 537 [km/u]
approach speed 3048 - 500 [m] (clean): 463 [km/u]
stalling speed clean at 500 [m] height at Max.Landing Weight : 58967 [kg]): 293 [km/u]
final approach speed at sea-level with full flaps (normal landing weight) (Vapp): 247
[km/u]
Airport Approach Category (APC) : C
landing speed at sea-level (normal landing weight(Vtd): 58767 [kg]): 219 [km/hr]
stalling speed at sea-level with full flaps (normal landing weight): 190 [km/u]
rate of climb at sea-level ROC (loaded) : 769 [m/min]
rate of climb at 1000 [m] with 1 engine out (PUF / MTOW) : 340 [m/min]
rate of descent: 457 [m/min]
calculation : *9* (regarding various performances)
high wheel pressure, can only take off from paved runways
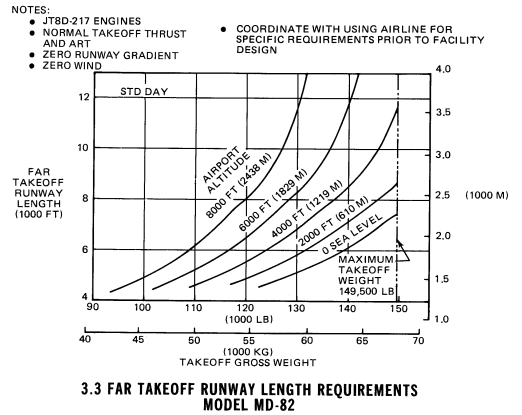
Runway length MTOW, sea level, standard day : 2300 [m], JT8D-217 engines
take-off distance at sea-level concrete runway : 2135 [m]
take-off distance at sea-level over 15 [m] height : 2293 [m]
landing run : 961 [m]
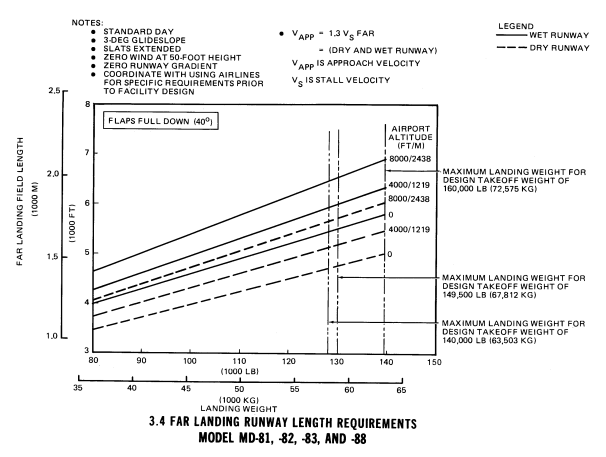
Landing field length ca. 1400 [m], max. landing weight, standard day, full flaps 40° : 1400 [m]
landing run (C.A.R.) from 15 [m] at SL, dry runway : 1357 [m]
landing run (C.A.R.) from 15 [m] at SL, wet runway : 1657 [m]
lift/drag ratio : 12.84 [ ]
climb to 5000 [m] with max payload : 6.02 [min]
climb to 10000 [m] with max payload : 18.51 [min]
descent time from 10000 [m] to 250 [m] : 24.33 [min]
theoretical ceiling fully loaded (mtow- 60 min. fuel:64288 [kg] ) : 15600 [m]
calculation *10* (action radius & endurance)
range with max. payload: 2889 [km] with 19969.0 [kg] max. useful load (70.5 [%] fuel)
range with high density pax: 3913 [km] with 170 passengers (94.2 [%] fuel)
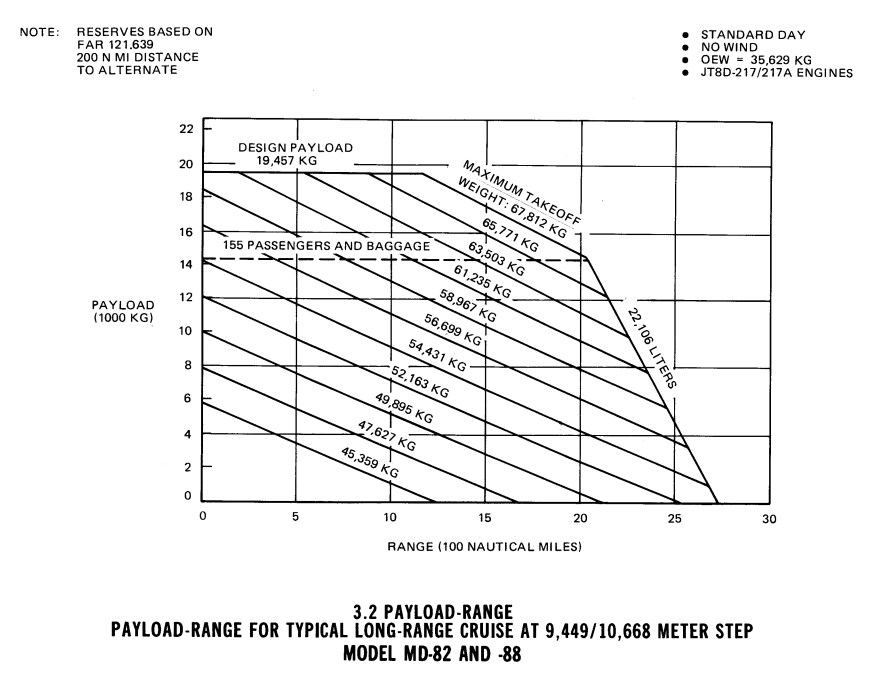
range with typical two-class pax: 4208 [km] with 143 passengers (100.0 [%] fuel)
range with max.fuel : 4170 [km] with 7 crew and 158 passengers and 100.0 [%] fuel
ferry range : 4560 [km] with 2 crew and zero payload (100.0 [%] fuel)
max range theoretically with additional fuel tanks total 41561.1 [litre] fuel : 8210 [km]
Available Seat Kilometres (ASK) : 601742 [paskm]
useful load with range 1000km : 19969 [kg]
useful load with range 1000km : 170 passengers

Martinair MD-82 PH-MBZ landing at Schiphol with thrust reversers deployed
production (theor.max load): 17433 [tonkm/hour]
production (useful load): 17433 [tonkm/hour]
production (passengers): 124839 [paskm/hour]
oil and fuel consumption per tonkm : 0.203 [kg]
fuel cost per paskm : 0.028 [eur]
crew cost per paskm : 0.007 [eur]

economic hours : 22300 [hours] is less then design hours
time between engine failure : 1030 [hr]
can continue fly on 1 engine, low risk for emergency landing for PUF
writing off per paskm : 0.010 [eur]
insurance per paskm : 0.0007 [eur]
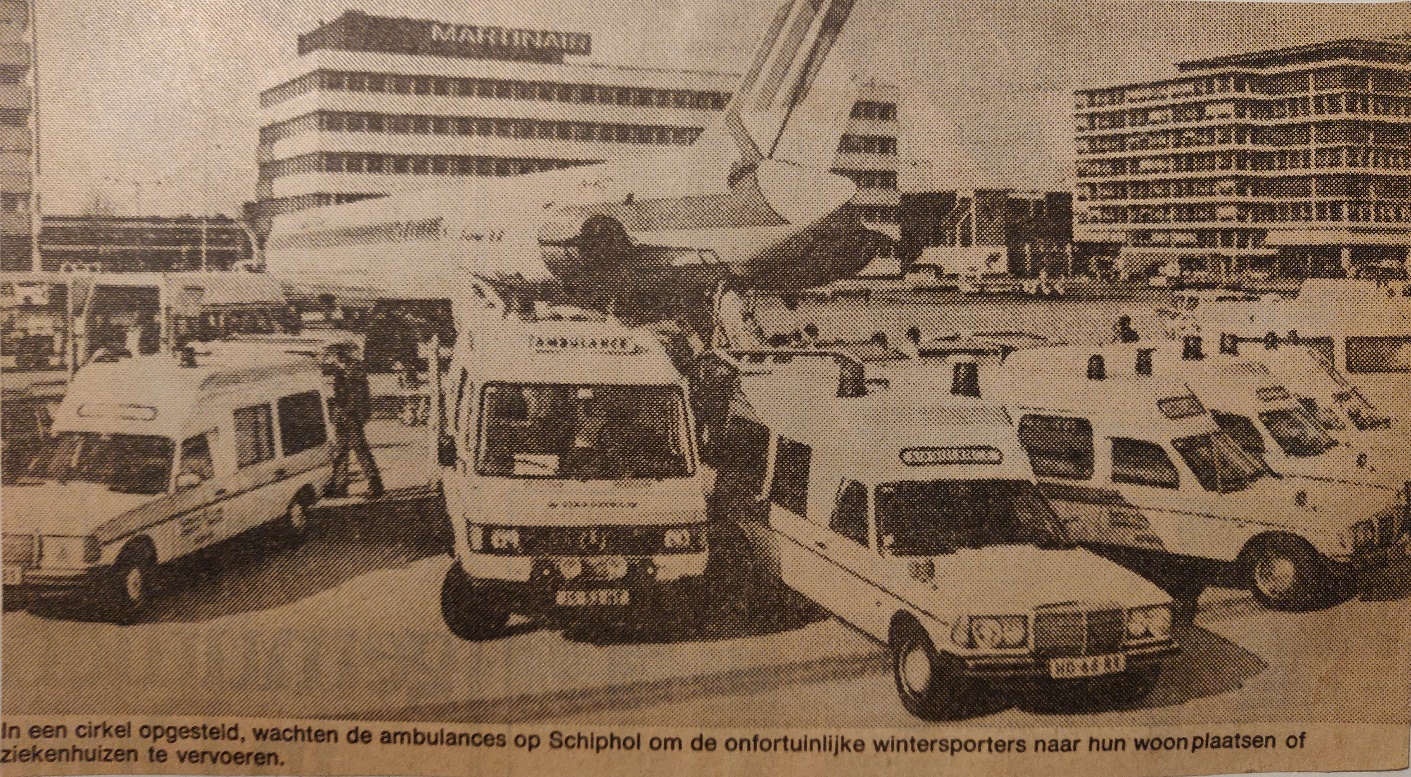

The MD-82 was used by Martinair to fly back to Holland unlucky wintersport tourist from the Alps.
maintenance cost per paskm : 0.014 [eur]
direct operating cost per paskm : 0.061 [eur]
direct operating cost per tonkm (max. load): 0.436 [eur]
direct operating cost per tonkm (normal useful load): 0.436 [eur]
The MD-82 was involved in several fatal accidents > see :
accident file (aircraftinvestigation.info)
Literature :
McDonnell Douglas MD-80 - Wikipedia
MCDONNELL DOUGLAS MD-82 | SKYbrary Aviation Safety
ICAO Aerodrome Reference Code | SKYbrary Aviation Safety
Approach Speed Categorisation | SKYbrary Aviation Safety
https://contentzone.eurocontrol.int/aircraftperformance/default.aspx ?
Jane’s all the world aircraft 1979-1980 page
https://www.boeing.com/search/results.html?q=airplane+characteristics
How to evaluate pavement strength using ACN-PCN (787guide.com)

Boarding of a Bulgarian Air MD-82
DISCLAIMER Above calculations are based on published data, they must be
regarded as indication not as facts.
Calculated performance and weight may not correspond with actual weights
and performances and are assumptions for which no responsibility can be taken.
Calculations are as accurate as possible, they can be fine-tuned when more data
is available, you are welcome to give suggestions and additional information
so we can improve our program. For copyright on drawings/photographs/
content please mail to below mail address
(c) B van der Zalm 22 October 2022 contact : info.aircraftinvestigation@gmail.com python 3.7.4