
Aircraft investigation >>>>>>> HOME PAGE
weight and performance calculations for the Douglas DC-8-53
***** PRELIMINARY FILE ****

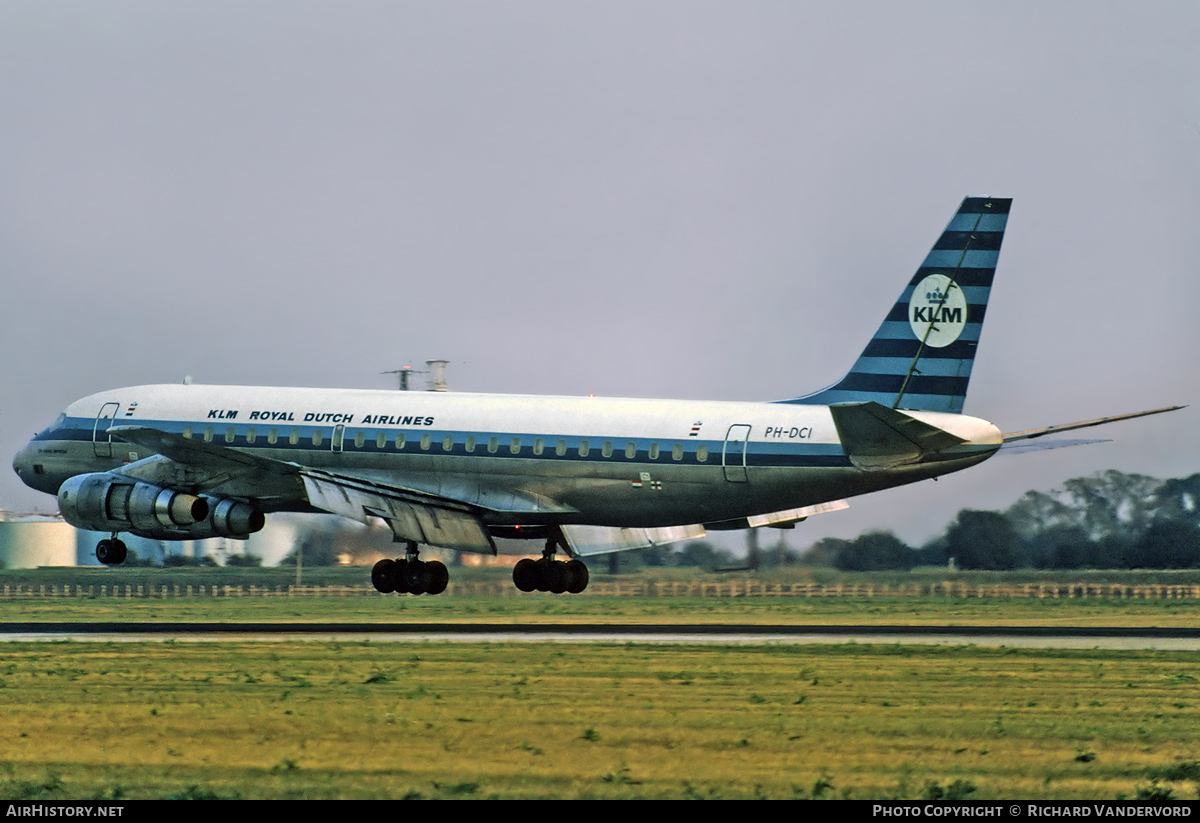
PH-DCI, the first DC-8-53 delivered to KLM.
Douglas DC-8-53
role : long range jet airliner
importance : ****
first flight : 20 December 1960 operational : May 1961
country : United States of America
design : head of design team Arthur Raymond (vice-president) and Ed Burton.
production : srs-50 : 89 aircraft, total DC-8 : 556 aircraft (1958-1972)
general information :
Pratt & Whitney developed out of the JT3C turbojet engine, a new variant, the JT3D. This was a turbofan engine, where the fan was attached to the low pressure compressor. This engine delivered more thrust while reducing fuel consumption by 1800 liters per hour resulting in a 15% greater range. The turbofan version of the DC-8 was designated -50.
There were a number of sub-variants:
-51 for domestic routes
-52 intercontinental JT3D-1 of 75.62 [KN] MTOW 136078 kgfor domestic routes while reducing consumption by 1800 litres per hour resulting in a 15% wider range. -53 intercontinental JT3D-3 of 80.07 [KN] MTOW 142900 kg
-54 freight version
-55 intercontinental JT3D-3B of 80.07 [KN] MTOW 147418 kg
In July 1959, KLM ordered a total of 5 -53s. At the beginning of April 1961 the first example was delivered, the PH-DCI "Sir Isaac Newton". That same year, however, KLM ran into financial problems. The number of employees had to be reduced from 19,000 in 1960 to 14,000 and the number of aircraft from 100 to 42. In 1961, KLM suffered a loss of NLG 75 million. There was a global malaise in aviation and the airlines had the greatest difficulty in getting their new jets full and selling their outdated propellor aircraft favorably.
There were also problems with the DC-8. The new turbofan engines had quite a few maintenance problems. The fan's blades got tired too quickly and had to be modified. The -53 also still did not reach the promised range and the airfoil had to be changed, on top of the already ongoing "speed recovery program". The wing nose had to be changed so that the cord became 4% larger. As a result, the wing area increased by 10.41 m^2 to 267.84 m^2. As a result, the air resistance decreased and the range increased by 7%. If Douglas had not been in such a hurry in the race with Boeing and had taken some more wind tunnel tests, these costly problems would probably have been avoided. The hydraulic system was also changed so that the aircraft would no longer deviate from the runway. The adjustments were carried out in the winter of '61/'62 by KLM itself under the supervision of Douglas technicians.
As a result, the timetable became disrupted and the DC-8 had to be withdrawn from the polar route, which then had to be operated by the DC-7C. From the 148 th DC-8 onwards, these changes were made directly on the production line.
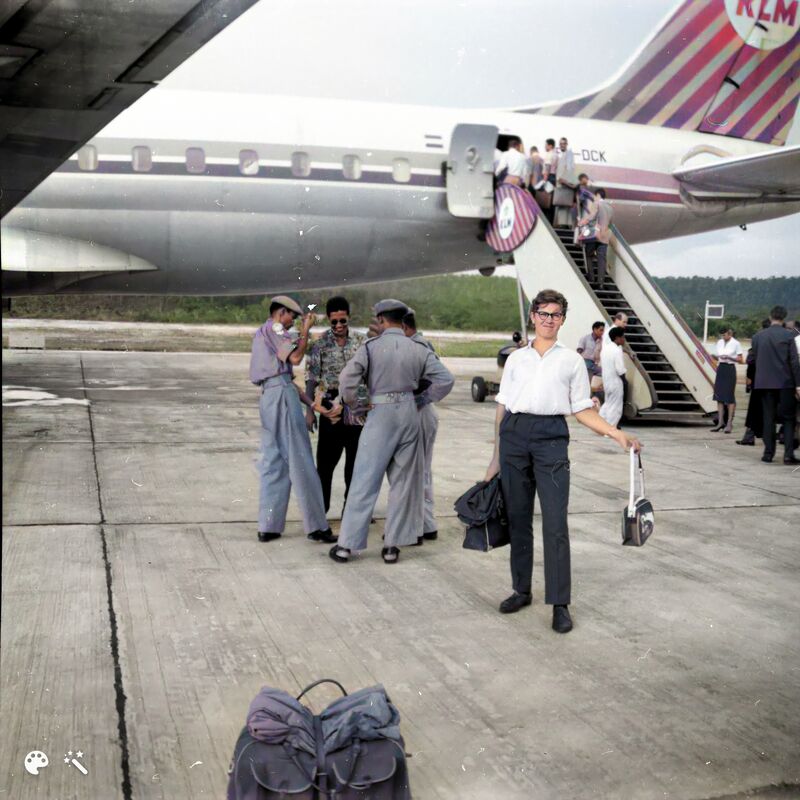

PH-DCK at Biak
In March and April 1962, DC-8-53s carried out a total of 9 clandestine flights to Dutch New Guinea, where an Indonesian invasion threatened. The U.S. supported Indonesia, so it was not possible to fly through Anchorage. The long flights went via the Azores, Curacao, Lima, Tahiti, Noumea and finally Biak.
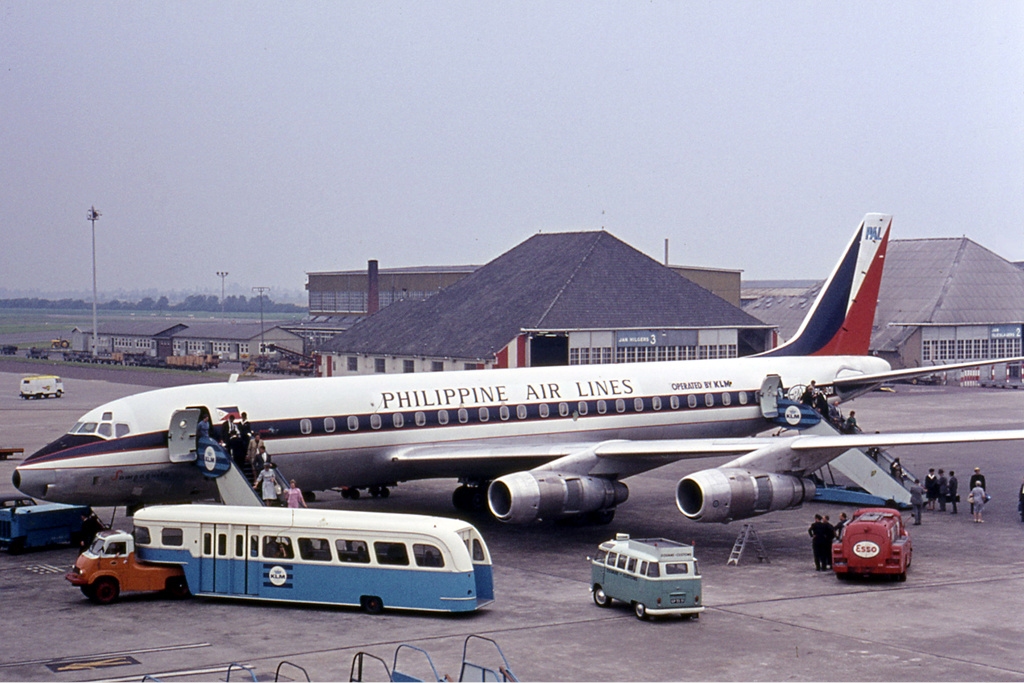

PI-C801, this was formerly the PH-DCP c/n 45608 at Schiphol airport, Amsterdam, July 1964
On February 23, 1962, the DC-8-53 "Pacific Pacer", the later PH-DCP, flew non-stop from Tokyo to Miami, a distance of 14010 km in 13 hours and 52 minutes. This was a new record for airliners. The average speed was 1010 km/h.
In the summer of 1965, KLM flew no less than 42 times a week over the Atlantic Ocean.
Landing speed (max.land weight) 246 km/h
primary users : KLM(9), VIASA, JAL, AVIACO
registrations :
KLM DC-8-53s :
PH-DCH "Orville Wright" c/n 45383 29 June 1968 burned out at Schiphol
PH-DCI "Sir Isaac Newton" c/n 45613 delivered as 1st April 1961
PH-DCK "Admiral Richard E.Byrd" c/n 45614
PH-DCL "Fridtjof Nansen" c/n 45615 30 May 1961 crashed near Portugal
PH-DCM "Henry Dunant" c/n 45616 was sold to VIASA in 1974
PH-DCN “Albert Schweizer” c/n 45629
PH-DCO "Sir Alexander Fleming" c/n 45632 Oct'79 last written out.
PH-DCP “Pacific Pacer” c/n 45608
PH-DCR "Gerard Mercator" c/n 45607
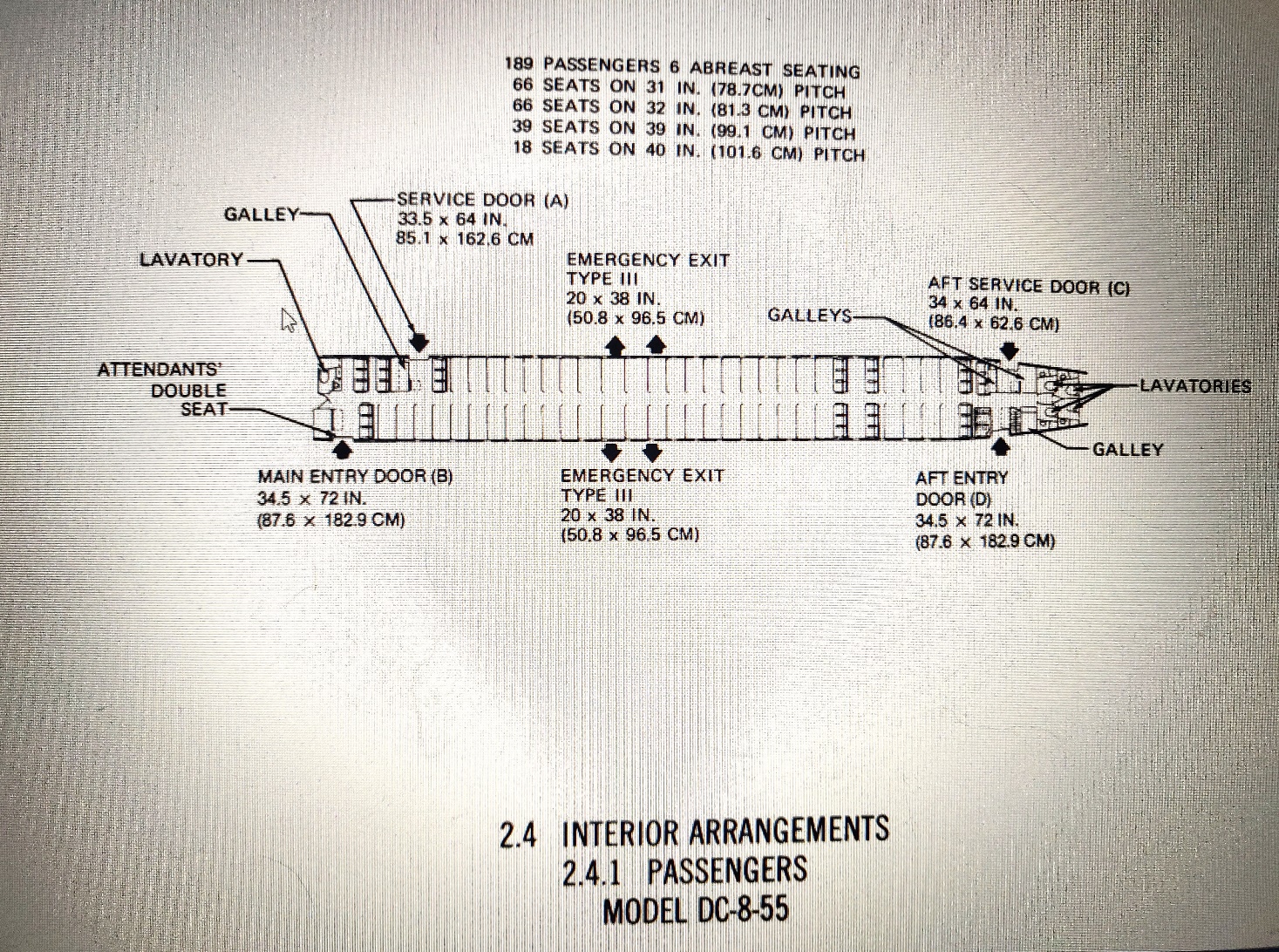
Accommodation:
flight crew : 4 cabin crew : 5
flight crew consist of pilot, co-pilot, navigator and flight engineer
passengers : seating for 136 in two class : 16 business class and 120 coach class seats ( 34 -in pitch)
high density seating for 189 passengers
engine : 4 Pratt & Whitney JT3D-3 turbofan engines of 80.07 [KN](18000.1 [lbf])
dimensions :
wingspan : 43.41 [m], length : 45.87 [m], height : 13.21 [m]
wing area : 267.84 [m^2] fuselage exterior width : 3.73 [m]
weights :
empty weight : 60781 [kg]
operating empty weight : 62717 [kg] max. structural payload : 23467 [kg]
Zero Fuel weight (ZFW) : 86184 [kg] max. landing weight (MLW) : 93900 [kg]
max.take-off weight : 142900 [kg] weight fuel : 70842 [kg] (88552 [liter])
performance :
Max. operating Mach number (Mmo) : 0.88 [Mach] (960 [km/hr]) at 9000 [m]
normal cruise speed : 926 [km/hr] (Mach 0.85 ) at 9144 [m] (39 [%] power)
service ceiling : 12000 [m]
range with max fuel : 6547 [km] and allowance for 755.2 [km] diversion and 30 [min] hold
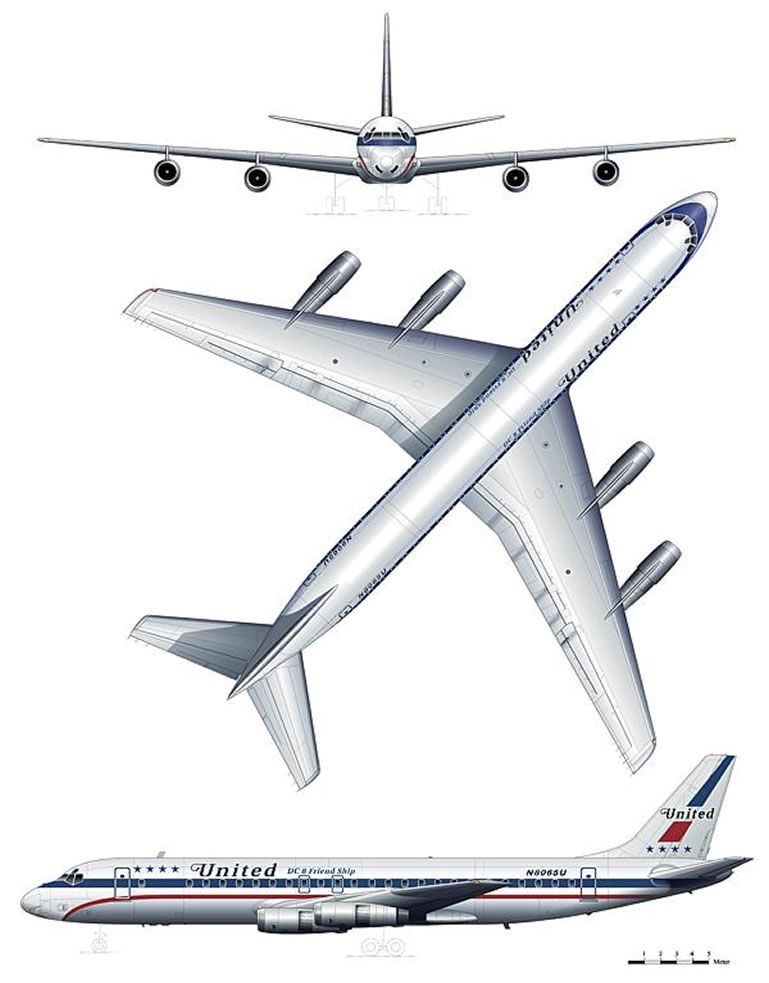

United airlines DC-8-52
description :
low-wing cantilever monoplane with retractable landing gear with nose wheel
tapered multi-cellular wing with flush-riveted stressed skin
with Fowler flaps airfoil : NACA
sweep angle 3/4 chord: 30.9 [°]
engines attached with pylons to the wing, main landing gear attached to the wings, fuel tanks in the wings and fuselage
construction : all-metal aluminium-alloy stressed-skin construction with pressurized fuselage
fuselage shape : 0
calculation : *1* (dimensions)
measured wing chord : 6.17 [m] at 50% wingspan
mean wing chord : 6.17 [m]
calculated average wing chord tapered wing with rounded tips: 6.07 [m]
wing aspect ratio : 7.04 []
seize (span*length*height) : 26304 [m^3]
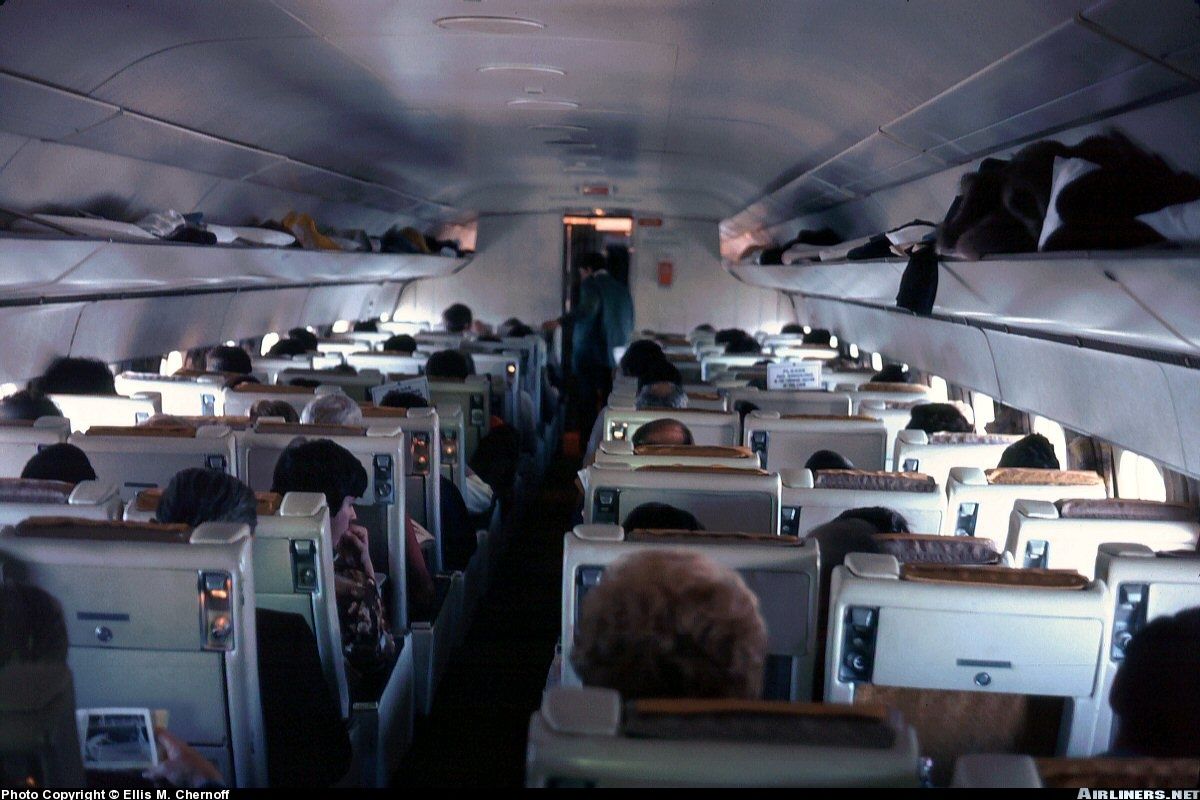

DC-8-51 interior
calculation : *2* (fuel consumption)
oil consumption : 32.0 [kg/hr]
fuel consumption (econ. cruise speed) : 8828.6 [kg/hr] (11035.8 [litre/hr]) at 39 [%] power
distance flown for 1 kg fuel : 0.10 [km/kg] at 9144 [m] height, sfc : 70.0 [kg/KN/h]
total fuel capacity : 88552 [litre] (70842 [kg])
calculation : *3* (weight)
weight engine(s) dry : 7440.0 [kg] = 23.23 [kg/KN]
weight 309.4 litre oil tank : 26.30 [kg]
oil tank filled with 2.0 litre oil : 1.8 [kg]
oil in engine 53.5 litre oil : 48.0 [kg]
fuel in engine 39.3 litre fuel : 28.83 [kg]
weight fuel lines 88.6 [kg]
weight engine cowling 960.8 [kg]
total weight propulsion system : 8594 [kg](6.0 [%])
***************************************************************
fuselage aluminium frame : 15792 [kg]
floor loading : 239 [kg/m2]
typical cabin layout for 136 passengers : economy : pitch : 86 [cm] ( 3+3 ) seating in 23.2 rows
pax density (normal seating) : 0.72 [m2/pax]
high density seating passengers : 186 at 6 -abreast seating in 31.1 rows, pitch 81.3 [cm]
weight 4 toilets : 55.2 [kg]
weight 7 hand fire extinguisher : 20 [kg]
weight 2 galleys : 134.6 [kg]
weight overhead stowage for hand luggage : 47.6 [kg]
weight 3 closets : 27.2 [kg]
weight 48 windows : 43.6 [kg]
weight 4 over wing emergency exits : 129.2 [kg]

weight lifejackets : 61.2 [kg]
weight oxygen masks & oxygen generators : 88.4 [kg]
weight emergency flare installation : 10 [kg]
weight 4 emergency evacuation slides : 63.4 [kg]
weight 4 entrance/exit doors : 301.5 [kg]
weight 2 freight doors (belly) : 107.7 [kg]
cabin volume (usable), excluding flight deck : 269.06 [m3]
passenger cabin max.width : 3.51 [m] cabin length : 31.10 [m] cabin height : 2.19 [m]
floor area : 98.4 [m2]
pressure difference :0.62 [kg/cm2]
weight rear pressure bulkhead : 206.2 [kg]
weight air pressurization system : 59.8 [kg]
fuselage covering ( 366.7 [m2] duraluminium 3.58 [mm]) : 3470.6 [kg]
weight floor beams : 587.7 [kg]
weight cabin furbishing : 858.0 [kg]
weight cabin floor : 1495.0 [kg]
fuselage (sound proof) isolation : 266.3 [kg]
weight radio transceiver equipment : 7.0 [kg]
weight dual cloud-collision radar : 25.0 [kg]
weight radio direction finding (RDF) equipment : 5.0 [kg]
weight Sperry Integrated Flight System : 11.0 [kg]
weight artificial horizon : 1.1 [kg]
weight instruments. : 38.0 [kg]
weight APU / engine starter: 40.0 [kg]
weight lighting : 34.0 [kg]
weight electricity generator : 34.0 [kg]
weight controls : 18.7 [kg]
weight seats : 725.0 [kg]
weight 44276 [litre] main central fuel tanks empty : 2479.5 [kg]
weight air conditioning : 204 [kg]
total weight fuselage : 27107 [kg](19.0 [%])
***************************************************************
total weight aluminium ribs (1183 ribs) : 5096 [kg]
weight engine mounts : 160 [kg]
weight fuel tanks empty for total 44276 [litre] fuel : 2479 [kg]
weight wing covering (painted aluminium 2.31 [mm]) : 3334 [kg]
total weight aluminium spars (multi-cellular wing structure) : 5230 [kg]
weight wings : 13660 [kg]
weight wing/square meter : 51.00 [kg]
weight rubber de-icing boots : 47.8 [kg]
weight fin & rudder (21.9 [m2]) : 1118.8 [kg]
weight stabilizer & elevator (30.1 [m2]): 1538.8 [kg]
weight flight control hydraulic servo actuators: 74.6 [kg]
weight fowler flaps (17.1 [m2]) : 440.8 [kg]
total weight wing surfaces & bracing : 19521 [kg] (13.7 [%])
*******************************************************************
wielen naar verhouding erg licht
wheel pressure : 15719.0 [kg]
weight 8 Dunlop main wheels (1130 [mm] by 226 [mm]) : 1069.9 [kg]
weight 2 Dunlop nose wheels : 133.7 [kg]
weight hydraulic wheel-brakes : 86.2 [kg]
weight pneumatic-hydraulic shock absorbers : 114.9 [kg]
weight wheel hydraulic operated retraction system : 1173.0 [kg]
weight undercarriage struts with axle 3228.4 [kg]
total weight landing gear : 5806.1 [kg] (4.1 [%]
*******************************************************************

********************************************************************
calculated empty weight : 61028 [kg](42.7 [%])
weight oil for 8.5 hours flying : 271.7 [kg]
weight catering : 336.5 [kg]
weight water : 269.2 [kg]
weight crew : 729 [kg]
weight crew lugage,nav.chards,flight doc.,miscell.items : 83 [kg]
operational weight empty : 62717 [kg] (43.9 [%])
********************************************************************
weight 136 passengers : 10472 [kg]
weight luggage : 2176 [kg]
weight cargo : 10819 [kg]
zero fuel weight (ZFW): 86184 [kg](60.3 [%])
weight fuel for landing (0.9 hours flying) : 7716 [kg]
max. landing weight (MLW): 93900 [kg](65.7 [%])
max. fuel weight : 133559 [kg] (93.5 [%])
payload with max fuel : 100 passengers+luggage 9341 [kg]
published maximum take-off weight : 142900 [kg] (100.0 [%])

KLM DC-8-53 PH-DCR c/n 45607 at New York – JFK apt.
calculation : * 4 * (engine power)
power loading (Take-off) : 446 [kg/KN]
power loading (operational without useful load) : 370 [kg/kN]
power loading (Take-off) 1 PUF: 595 [kg/KN]
max. total take-off power : 320.3 [KN]
calculation : *5* (loads)
manoeuvre load : 8.7 [g] at 1000 [m]
limit load : 3.0 [g] ultimate load : 4.5 [g] load factor : 0.8 [g]
design flight time : 4.95 [hours]
design cycles : 1675 sorties, design hours : 8291 [hours]
operational wing loading : 4330 [N/m^2]
wing stress (3 g) during operation : 255 [N/kg] at 3g emergency manoeuvre
calculation : *6* (angles of attack)
angle of attack zero lift : -1.80 ["]
max. angle of attack (stalling angle, clean) : 13.98 ["]
angle of attack at max. speed : 1.34 ["]
calculation : *7* (lift & drag ratios
lift coefficient at angle of attack 0° : 0.15 [ ]
lift coefficient at max. speed : 0.26 [ ]
lift coefficient at max. angle of attack : 1.31 [ ]
max. lift coefficient full flaps : 1.58 [ ]
induced drag coefficient at max.speed : 0.0041 [ ]
drag coefficient at max. speed : 0.0312 [ ]
drag coefficient (zero lift) : 0.0272 [ ]
lift/drag ratio at max. speed : 8.37 [ ]
calculation : *8* (speeds
stalling speed at sea-level (OW loaded : 134071 [kg]): 281 [km/u]
stalling speed at sea-level with full flaps (normal landing weight): 214 [km/u]
V : 395.63 te laag, Cl > Clmax berekening PR nodig klopt niet meer cl : 1.41 line 216
flying weight (fw) : 107581.0
landing speed at sea-level (normal landing weight : 93597 [kg]): 246 [km/hr]
max. rate of climb speed : 574 [km/hr] at sea-level
max. endurance speed : 396 [km/u] min. fuel/hr : 5925 [kg/hr] at height : 2438 [m]
max. range speed : 799 [km/u] min. fuel consumption : 8.571 [kg/km] at cruise height : 10058 [m]
cruising speed : 926 [km/hr] at 9144 [m] (power:38 [%])
max. operational speed (Mmo) : 960.00 [km/hr] (Mach 0.88 ) at 9000 [m] (power:42.3 [%])
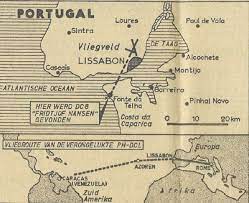
KLM had started a partnership with the Venezuelan VIASA and lent a DC-8 to this carrier. On May 30, 1961, the brand new PH-DCL " Fridtjof Nansen " c/n 45615 in service of VIASA crashed. It was with 47 passengers and 14 crew members on its way from Rome to Caracas, via Madrid, Lisbon and the Azores. After the nightly start of Portelo RW23 near Lisbon, the aircraft fell into severe thunderstorms. It crashed 5 minutes after the start, 7km south of the LS radio beacon Caparcia, 3.5km off the coast near the town of Fonte de Telha into the sea. South of the Tagus estuary, in Caparica Bay in 30m deep water. All occupants are killed. 75% of the wreck was recovered. The aircraft had only made 193 flight hours. The cause of the disaster has never been fully clarified. Perhaps the artificial horizon has failed.
Location : +-1km 38°34'11"N 9°13'39"W
airflow : 675.0 [kg/s]
speed of thrust jet : 1599 [km/hr]
climbing speed at sea-level (loaded) : 1547 [m/min]
climbing speed at 1000 [m] with 1 engine out (PUF / MTOW) : 1232 [m/min]
climbing speed at 1000 [m] with 2 engines out (2xPUF / MTOW) : 1184 [m/min]
calculation : *9* (regarding various performances)
take-off speed : 348.4 [km/u]
high wheel pressure, can only take off from paved runways
take-off distance at sea-level concrete runway : 2113 [m]
take-off distance at sea-level over 15 [m] height : 2206 [m]
landing run : 1173 [m]
landing run from 15 [m] : 2042 [m]
lift/drag ratio : 12.45 [ ]
max. theoretical ceiling : 17800 [m] with flying weight :134071 [kg] line 3359
climb to 1000m with max payload : 0.78 [min]
climb to 2000m with max payload : 1.52 [min]
climb to 3000m with max payload : 2.22 [min]
climb to 5000 [m] with max payload : 3.49 [min]
minimum flying speed at 12000 [m] : 633 [km/hr]
theoretical ceiling fully loaded (mtow- 60 min. fuel:134071 [kg] ) : 17800 [m]
calculation *10* (action radius & endurance)
published range : 6547 [km] with 9 crew and 17763 [kg] useful load and 88.1 [%] fuel
range : 5949 [km] with 23467.0 [kg] max. useful load (80.1 [%] fuel)
range : 7083 [km] with 136.0 passengers with each 16 [kg] luggage and 95.3 [%] fuel
range max. fuel : 7430 [km] with 9341.4 [kg] useful load and 100.0 [%] fuel
Available Seat Kilometres (ASK) : 963353 [paskm]
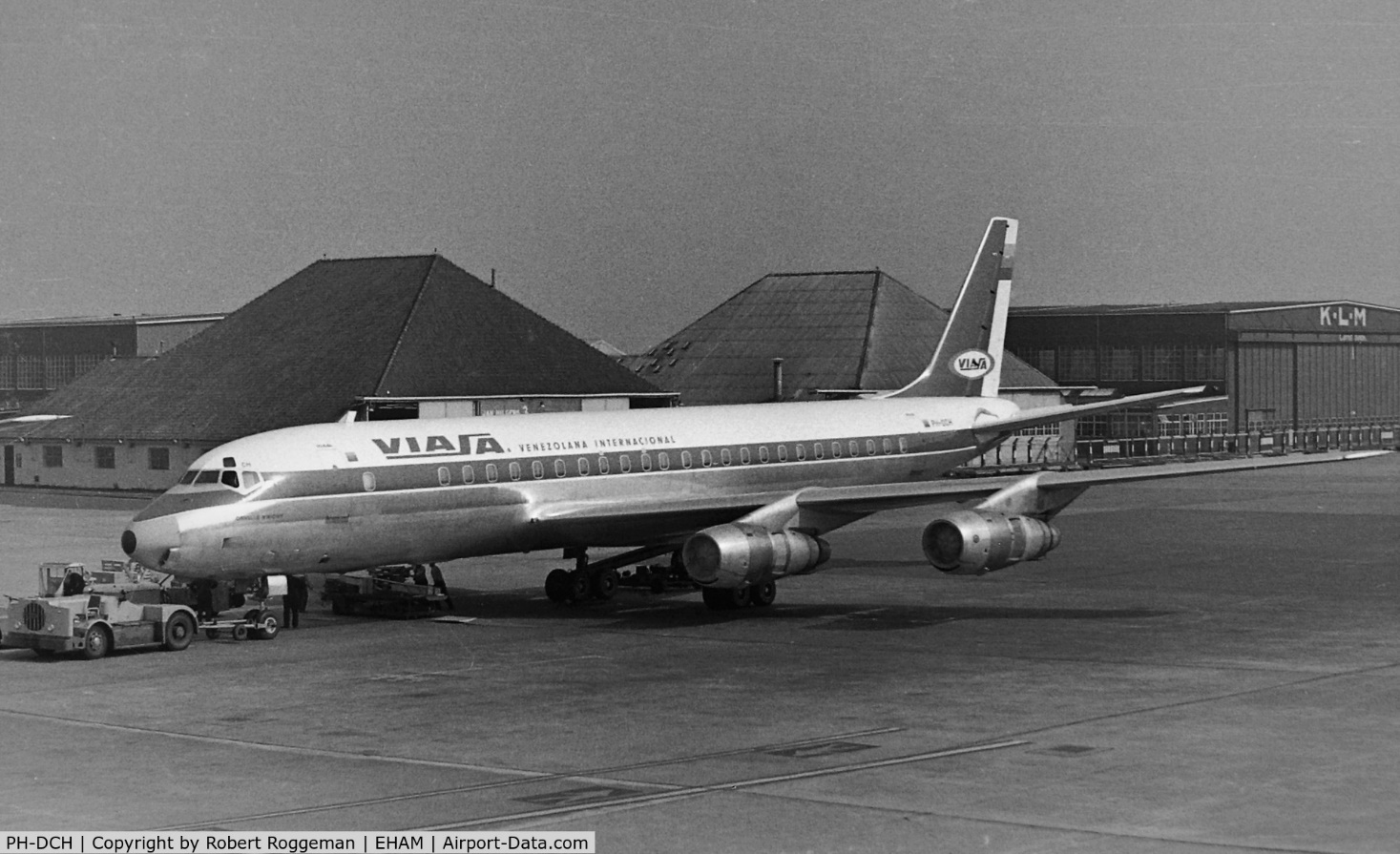

PH-DCH at Schiphol Amsterdam airport
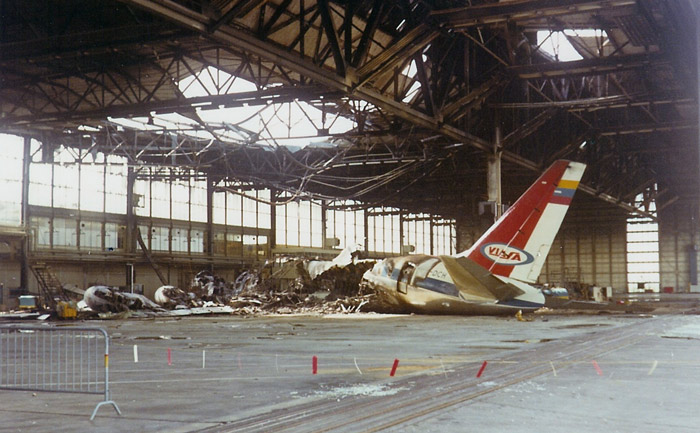
On the night of June 28-29, 1968, the DC-8-53 PH-DCH "Orville Wright" c/n 45383 went up in flames after an explosion while in hangar 10. The DC-9 PH-DNN was also severely damaged. The PH-DCH (first flight 1960) had made 23668 flight hours at that time and had been leased to VIASA at the time of the fire. The cause has not been determined with certainty. Maybe it was a discharge of static electricity in the right full wing tank, or short circuit in the wiring or a fault of a mechanic. Location : +-150m 52°18'04.90"N 4°47'32.38"E

max range theoretically with additional fuel tanks total 100228.8 [litre] fuel : 9355 [km]
useful load with range 500km : 75416 [kg]
useful load with range 500km : 136 passengers
production (theor.max load): 69835 [tonkm/hour]
production (useful load): 21730 [tonkm/hour]
production (passengers): 125936 [paskm/hour]
combi aircraft mail/freight/passengers
oil and fuel consumption per tonkm : 0.127 [kg]
fuel cost per paskm : 0.070 [eur]
crew cost per paskm : 0.010 [eur]
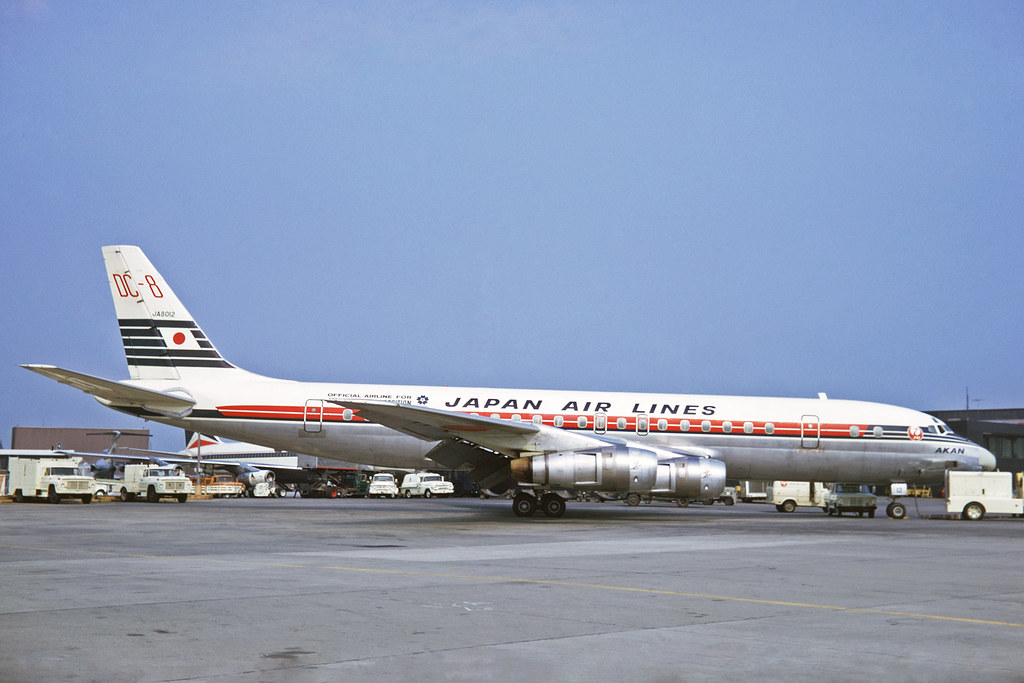

JA8012 at New York JFK apt, July 1970
On June 14, 1972, the DC-8-53 JA8012 “Akan” c/n 45680 of the JAL crashed near New Delhi. Had taken off with 76 passengers and 11 crew members in Bangkok (BKK) as flight 471 to Delhi. Plane makes an approach to RW28 Delhi – Palam airport (DEL) but crashes into bank of the Yamuna river 20km east of the airport. 82 passengers are killed and 4 people on the ground.
The aircraft had made its first flight in 1964. According to the Japanese, the accident was caused by a wrong ILS signal. However, the Indian authorities placed the blame on the crew, who would have followed a wrong approach procedure and misinterpreted their instruments. Location +-100m 28°32'04.44"N 77°19'44.11"E
time between engine failure : 481 [hr]
can continue fly on 3 engines, low risk for emergency landing for PUF
writing off per paskm : 0.049 [eur]
insurance per paskm : 0.0007 [eur]
maintenance cost per paskm : 0.037 [eur]
direct operating cost per paskm : 0.166 [eur]
direct operating cost per tonkm (max. load): 0.300 [eur]
direct operating cost per tonkm (normal useful load): 0.965 [eur]
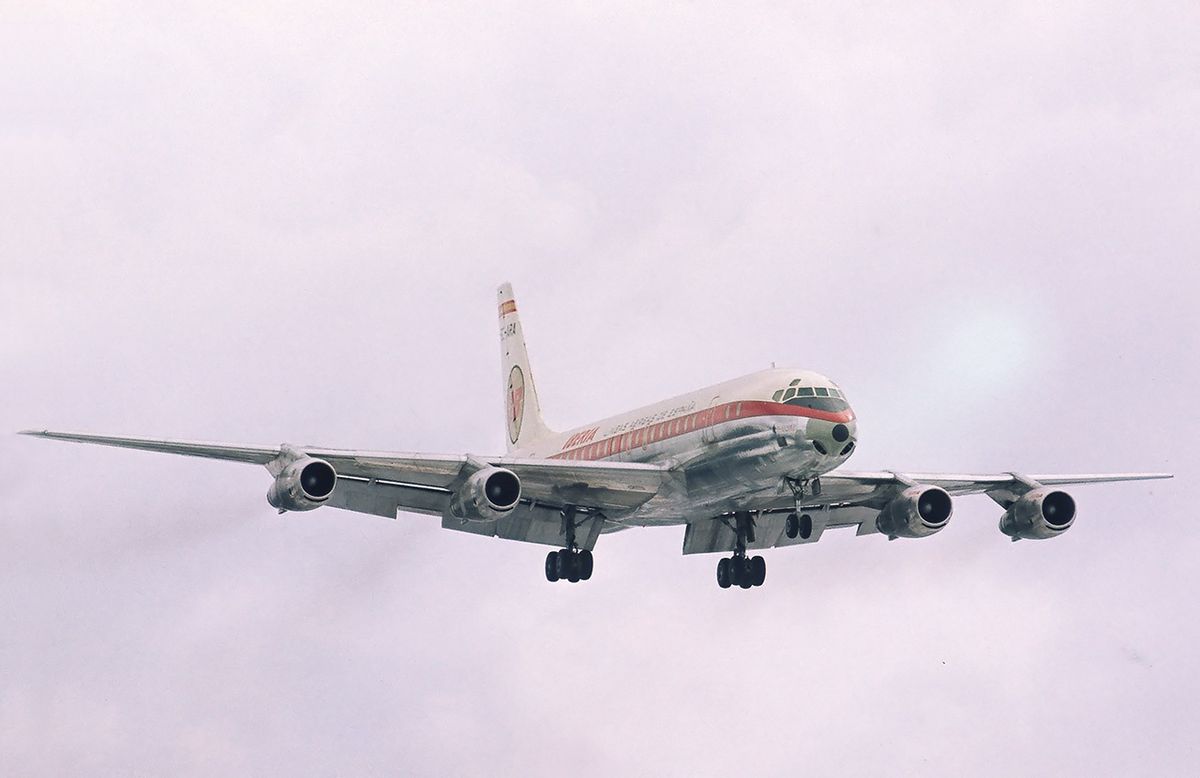

EC-ARA on short final to RWY 01 Arlanda apt., Stockholm, February 1969
On July 06, 1972, the DC-8-52 EC-ARA c/n 45617 of AVIACO plunges into the Atlantic Ocean, 22.5km east of Las Plamas, Canary Islands. Performed a re-position flight 331 from Madrid (MAD) to Las Palmas (LPA) and had no passengers on board, only 10 crew members, all of whom died.
1st flight 1961 Location : +-500m 28°08'57"N 15°11'46"W
Literature :
Wikipedia
verkeersvliegtuigen (Moussault) page 88,157
De Nederlandse DC-8 vliegtuigen page 1 - 33
Praktisch handboek vliegtuigen deel 5 page 65
Wat is dat voor een vliegtuig ? page 86
Jane’s commercial transport aircraft page183
Jane’s all the world aircraft ’64-’65 page 212 www.aviation-safety.net
Fridtjof Nansen (aviacrash.nl)
Mokmer Biak Nw. Guinea - ONZE MARINE VLOOT (weebly.com)
https://www.boeing.com/search/results.html?q=airplane+characteristics
DISCLAIMER Above calculations are based on published data, they must be
regarded as indication not as facts.
Calculated performance and weight may not correspond with actual weights
and performances and are assumptions for which no responsibility can be taken.
Calculations are as accurate as possible, they can be fine-tuned when more data
is available, you are welcome to give suggestions and additional information
so we can improve our program. For copyright on drawings/photographs/
content please mail to below mail address

KLM DC-8-53 RP-C803 picture taken at London, Heathrow, May 1977
(c) B van der Zalm 27 June 2022 contact : info.aircraftinvestigation@gmail.com python 3.7.4