Aircraft investigation >>>>>>> HOME PAGE
performance calculations for the Bristol Hercules 763 aircraft engine

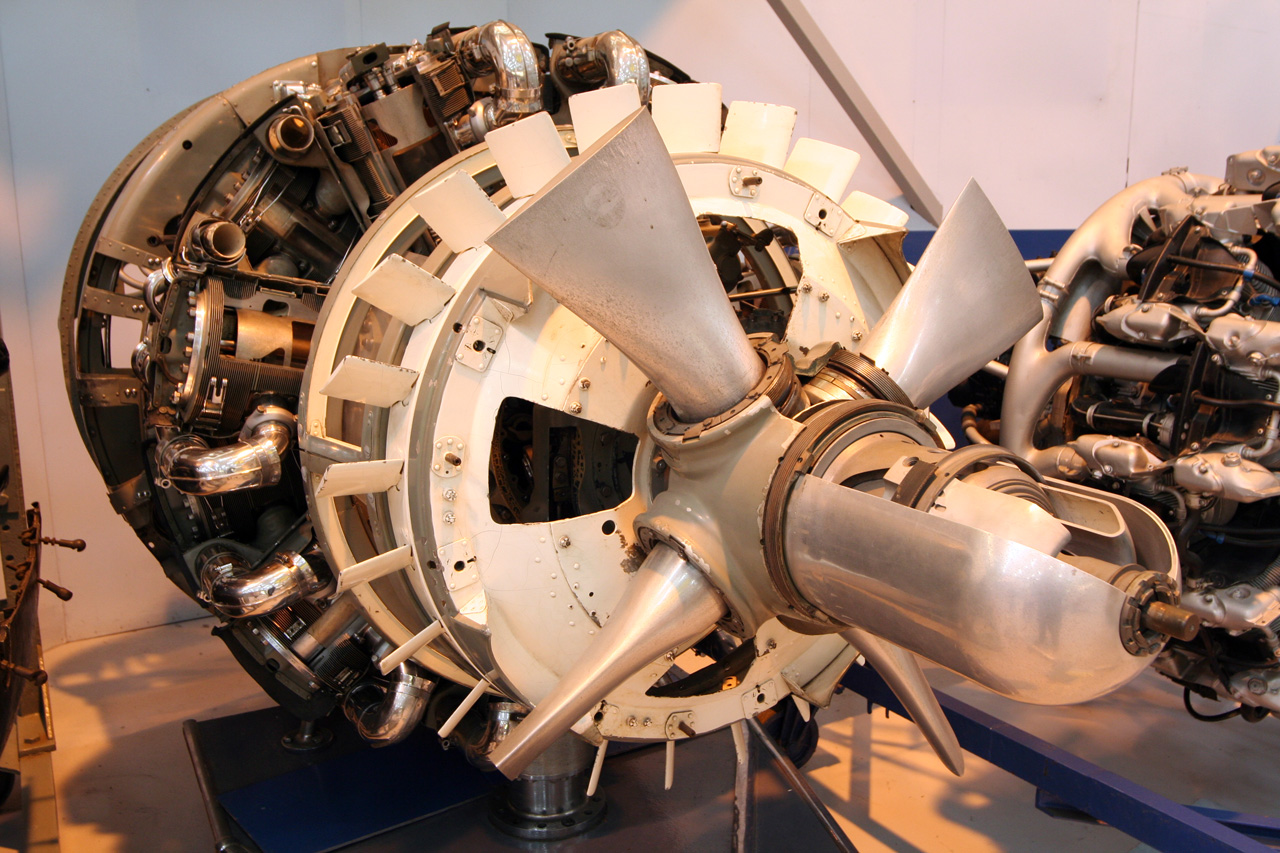
Bristol Hercules 763 air-cooled 14 -cylinder double row radial engine 1775 [hp]
(1323.6 KW)
gear-driven supercharger, constant power to height : 4000 [m] blower ratio : ?? [:1]
introduction : 1947 country : UK importance : ***
applications : Handley Page H.P.81 Hermes IV
normal rating : 1775 [hp](1323.6 KW) at 2800 [rpm] at 4000 [m] above sea level
take-off power : 2100 [hp] (1566.0 [KW]) at 2800 [rpm]
reduction : 0.44 , valvetrain : sleeve valves
weight engine(s) dry with reduction gear : 894.0 [kg] = 0.68 [kg/KW]
General information :
fuel system : fuel type : octane grade no. 100 oil system :
engine starter type :
bore : 146.0 [mm] stroke : 165.0 [mm]
supercharger compression ratio : 1.96 [ ]
valve inlet area : 39.0 [cm^2]
gasspeed at inlet valve : 46.5 [m/s]
blower speed : ???? [rpm] , mixture :13.0 :1
compression ratio: 7.00 :1
high octane fuel needed to prevent detonation
sleeve valve engine higher piston speed allowable
stroke volume (Vs displacement): 38.700 [litre]
compression volume (Vc): 6.445 [litre]
total volume (Vt): 45.118 [litre]
overall engine diameter: 132.0 [cm]
calculated engine length: 112.13 [m]
specific power : 34.2 [kW/litre]
torque : 4514 [Nm]
engine weight/volume : 23.1 : [kg/litre]
average piston speed (Cm): 15.4 [m/s]
***************************************************************************
intake manifold absolute pressure (MAP) at 4000 [m] altitude Pi (ata.) : 1.03 [kg/cm2]
(29.83 [inHg])
mean engine pressure (M.E.P.) at 4000 [m] altitude Pm : 12.39 [kg/cm2]
compression pressure at 4000 [m] altitude Pc: 11.73 [kg/cm2]
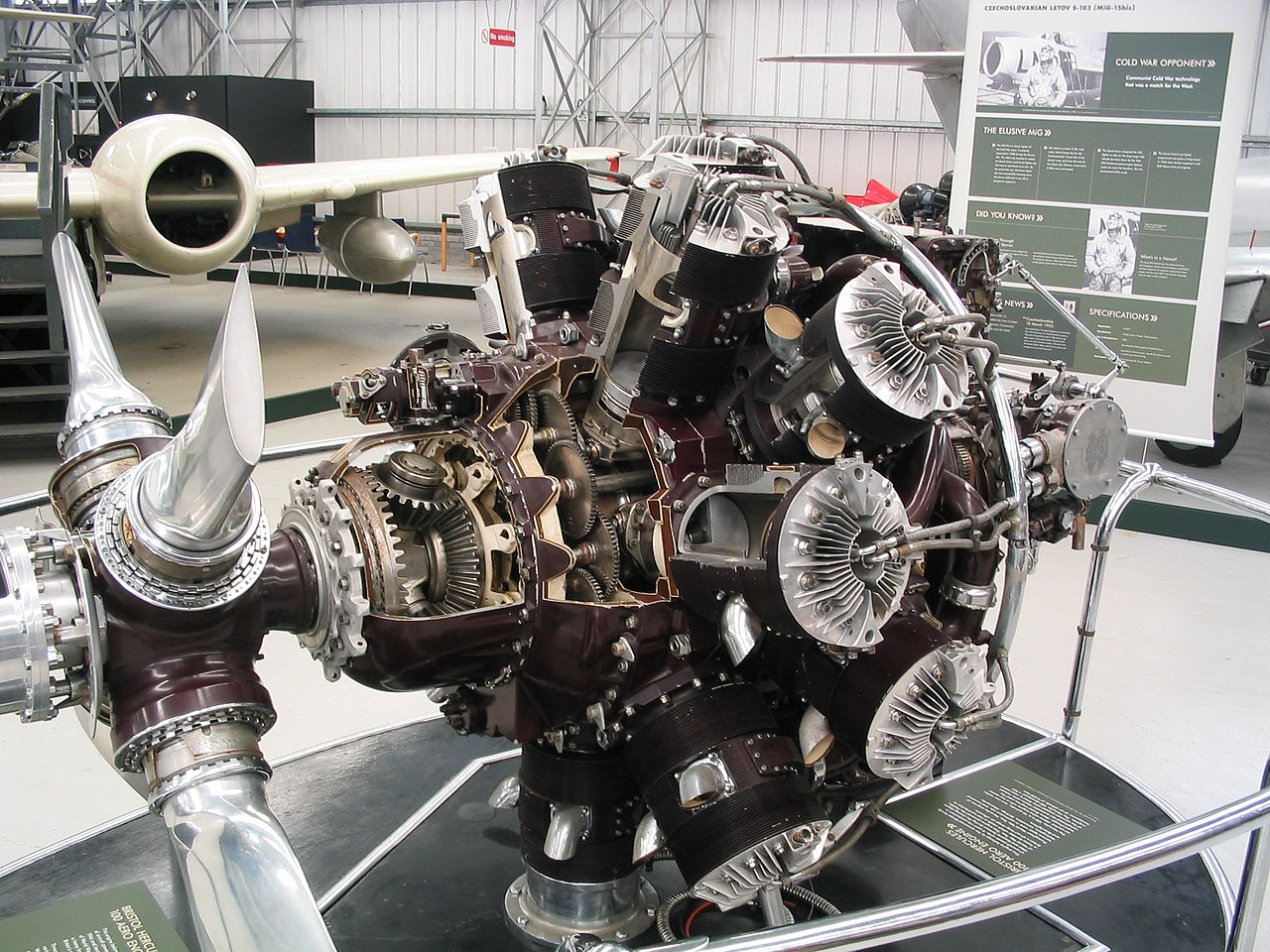
Bristol Hercules engine on display at the Museum of Flight, East Fortune, Scotland
estimated combustion pressure at 4000 [m] Pe : 46.85 [kg/cm2]
exhaust pressure at 4000 [m] Pu : 4.04 [kg/cm^2 ]
**************************************************************************
compression-start temperature at 4000 [m] Tic: 342 [°K] (69 [°C])
compression-end temperature at 4000 [m] Tc: 550 [°K] (276 [°C])
average engine wall temperature at 4000 [m] : 476 [K] (202 [°C])
caloric combustion temperature at 4000 [m] Tec: 2319 [°K] (2045 [°C])
polytroph combustion temperature at 4000 [m] Tep : 2195 [°K] (1922 [°C])
estimated combustion temperature at 4000 [m] Te (T4): 2230 [°K] (1957 [°C])
polytrope expansion-end temperature at 4000 [m] Tup: 1148 [°K] (875 [°C])
exhaust stroke end temperature at 4000 [m] Tu: 1114 [°K] (840 [°C])
*********************************************************************************
calculations for take-off/emergency power at sea level
average piston speed : 15.4 [m/s]
gasspeed at inlet valve : 46.5 [m/s]
intake pressure at sea level for Take-off Pi : 1.23 [kg/cm2] (35.62 [inHg])
max. intake pressure (full blower) at sea level for Take-off Pi : 2.02 [kg/cm2]
(58.55 [inHg])
rich mixture 11.5 : 1 applied for cooling > carburettor adjustable in flight by the pilot
caloric combustion temperature at sea level Tec: 2150 [°K] (1877 [°C])
insufficient cooling, can run max 2 minutes at this power before overheating
emergency/take off rating at 2800 [rpm] at sea level : 2100 [hp]
Thermal efficiency Nth : 0.385 [ ]
Mechanical efficiency Nm : 0.738 [ ]
Thermo-dynamic efficiency Ntd : 0.284 [ ]
design hours : 2251 [hr] time between overhaul : 964 [hr]

dispersed engine heat by cooling air : 15634.97 [Kcal/minuut/m2]
required cooling surface : 27.40 [m2]
weight cooling ribs : 84.77 [kg]
fuel consumption optimum mixture at 2800.00 [rpm] at 4000 [m]: 332.01 [kg/hr]
specific fuel consumption thermo-dynamic : 211 [gr/epk] = 284 [gr/kwh]
estimated specific fuel consumption (cruise power) at 4000 [m] : 295 [gr/kwh]
specific fuel consumption (volume*rpm at 1 atm MAP) at 2800 [rpm] : 231 [gr/kwh]
estimated specific oil consumption (cruise power) : 11 [gr/kwh]
Literature :
Jane’s fighting aircraft WWII page

DISCLAIMER Above calculations are based on published data, they must be
regarded as indication not as facts.
Calculated performance and weight may not correspond with actual weights
and performances and are assumptions for which no responsibility can be taken.
Calculations are as accurate as possible, they can be fine-tuned when more data
is available, you are welcome to give suggestions and additional information
so we can improve our program. For copyright on drawings/photographs/
content please mail to below mail address
(c) B van der Zalm 03 April 2022 contact : info.aircraftinvestigation@gmail.com python 3.7.4
notes :